In the past few years, Virtual reality (VR) is making headway into different industries and it is getting popular day by day.VR technology has been fully established in the gaming industry, and is increasingly been implemented in the healthcare industry. Application of VR for robotic surgery, healthcare devices, etc. are gradually gaining approval and are now more likely to be implemented by various healthcare organizations and the people.
Virtual Reality allows both healthcare professionals and patients totake part in simulated environments customized for medical education (including simulative surgery training), pain management or therapy. In 2020, the global healthcare VR market was estimated $336.9 million. It is projected to grow at an average CAGR of 30.7% and reach $2.2 billion by 2024.
Extreme demand for high-quality healthcare services is one of the main factors influencing the expanding use of VR in healthcare.The need to lower healthcare expenses and the impact of connected devices in healthcare has contributed to the rise of VR in healthcare.
Applications of virtual reality in medicine:
- Medical Education
Medical education and training have long made use of VR simulation technologies. The focus of modern medical education has changed from rote memorization of data to teaching students how to use those facts to determine the best course of action for a particular patient.
Virtual reality (VR) technology can be used to replicate any medical event, allowing students to respond to it as if it were real. Feedback and a debriefing are then given to help them, if necessary, learn from their mistakes. Medical experts can use VR to visualise the human body’s structure, opening up previously unreachable spaces. For starters, virtual reality studies of human anatomy have replaced the dissection of cadavers, which was once required of all fresher medical students. With the help of computer graphics, it is now possible to make exact replicas of any organ part in minute detail. Orthopaedic surgeon trainees can greatly benefit from understanding how fractures develop and worsen in real life.
- Virtual Reality in Diagnostics
VR is being used as a potent diagnostic tool that enables doctors and medical professionals to make precise diagnoses. This technique is used in conjunction with others, such as MRI/CT scans, and because no intrusive procedures are required, the patient has a pain-free experience.
- Mental Illness Treatment
One of the common methods for treating various forms of mental illness is exposure therapy. Due of its low cost, flexibility, and low-risk nature, virtual reality is gradually altering the way exposure therapy is administered to mentally ill patients. VR also aids in the treatment of anxiety and panic attacks by presenting fresh techniques to keep the body quiet and relaxed. For example, therapists and patients with phobias in mental health found VR to be quite beneficial.
- Pain Management
Medical professionals have long employed cognitive diversion techniques to manage various sorts of pain. By offering a variety of interactive games, VR gives traditional tactics of distraction a different aspect. These games have a plethora of interactive features and are played in a virtual setting. Virtual reality has also been proven to be helpful in the treatment of pain and rehabilitation of patients with severe discomfort, including those who are recovering from skin graft surgery, while daily cleaning burn wounds, or to make daily injections for kids more tolerable.
- Physical Fitness and Therapy
The way activities are performed now is drastically changing in the fitness sector. Numerous start-ups in the sector are redefining exercise by integrating VR with cardio programmes. Moving on, VR plays a significant role in physical rehabilitation, as patients are subjected to an exercise plan that uses VR rather than prescription medications or invasive procedures.
Virtual reality helps patients perform their exercises more easily, which shortens rehabilitation period during physical therapy as well. This is due to the fact that VR diverts the patient’s focus from their discomfort by offering an engaging alternate reality that simultaneously captivates, inspires, and urges them to finish the task.
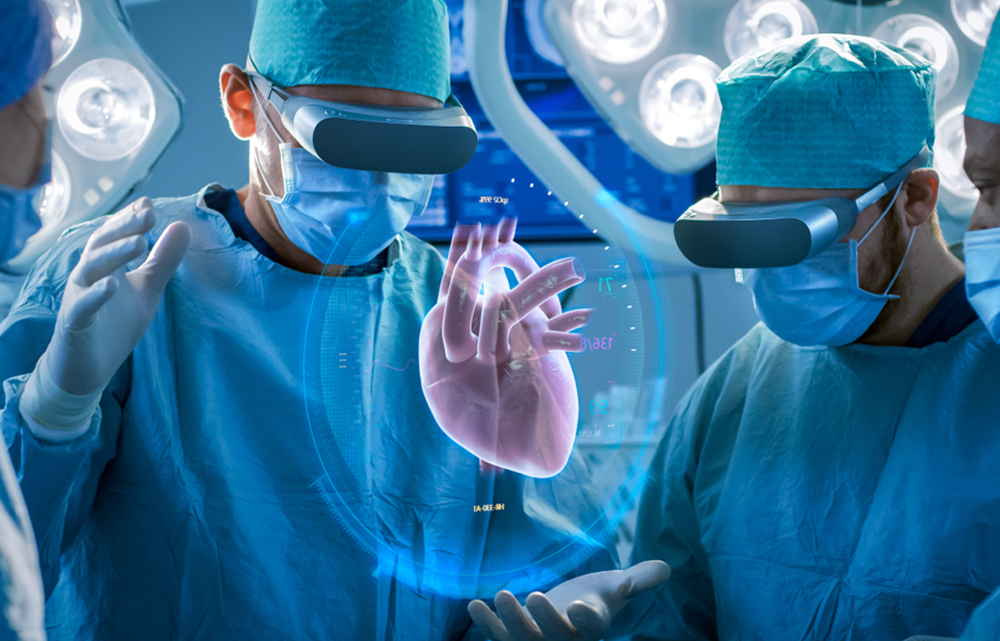
- Virtual Reality in Surgery
Virtual reality in surgery has been around for a while and has become extremely popular among medical professionals. A robotic surgical tool is used for the procedure, while the human surgeon controls the robotic device. By using this approach, the time and likelihood of surgical complications are minimized.
Virtual reality (VR) is predicted to be used more frequently in the future to boost the safety and efficiency of surgical operations, particularly minimally invasive or non-invasive ones, and to better comprehend the workings of the human body.
With virtual reality, the surgical team can perform their planned intervention and go through the entire treatment, which is helpful for planning complex surgeries like neurosurgery procedures.
The use of VR with tactile and sensory feedback is proven to be both safe and reproducible, as well as affordable, compared to conventional training, in the learning of suture application in operating rooms and orthopaedic procedures.
- Human Simulation Techniques
Doctors, physicians, nurses, and other medical personnel can engage with patients thanks to virtual reality (VR). Only in a 3D environment are they able to interact with patients and take part in various training exercises. This is an immersive experience that uses a number of sensors to ascertain the participant’s feelings.
- Other Applications
Doctors, nurses, and other medical professionals can use VR to help with various human simulation techniques. In addition to the uses already mentioned, virtual reality (VR) has a wide range of other applications in the medical field, including dentistry, PTSD treatment, nursing, autism treatment, and more.
AR and VR have been shown to have favourable effects on immersive learning throughout the healthcare spectrum, making them more than just fascinating new tools. Immersive technologies, like augmented surgery, will be employed more frequently in the upcoming years to increase the precision and efficacy of current operations. People’s capacities as caregivers and patients will be improved, and they will have access to life-saving knowledge and essential skills in ways that no other technology can match. Only the inventiveness and originality of individuals who develop and use the technology will be able to fully realise VR’s promise in the healthcare industry. Tools for virtual reality will close gaps rather than create them, and in the end, the virtual will contribute to making us all more human.

